Below, we're compiled a handy checklist for external audits of your company’s ESG performance.
1. Understanding organizational context
Before diving into the audit, take the time to understand your organization's context. Assess the industry landscape, identify relevant stakeholders, and familiarize yourself with existing ESG policies and objectives within your company. This understanding provides valuable context for selecting the right framework (point 2).
Sweep can help you to:
-
Understand industry trends, identify stakeholders, and establish ESG oversight.
-
Determine the significance of ESG factors and identify key responsible parties.
-
Engage stakeholders from the start and promote cross-functional cooperation for ESG initiatives.
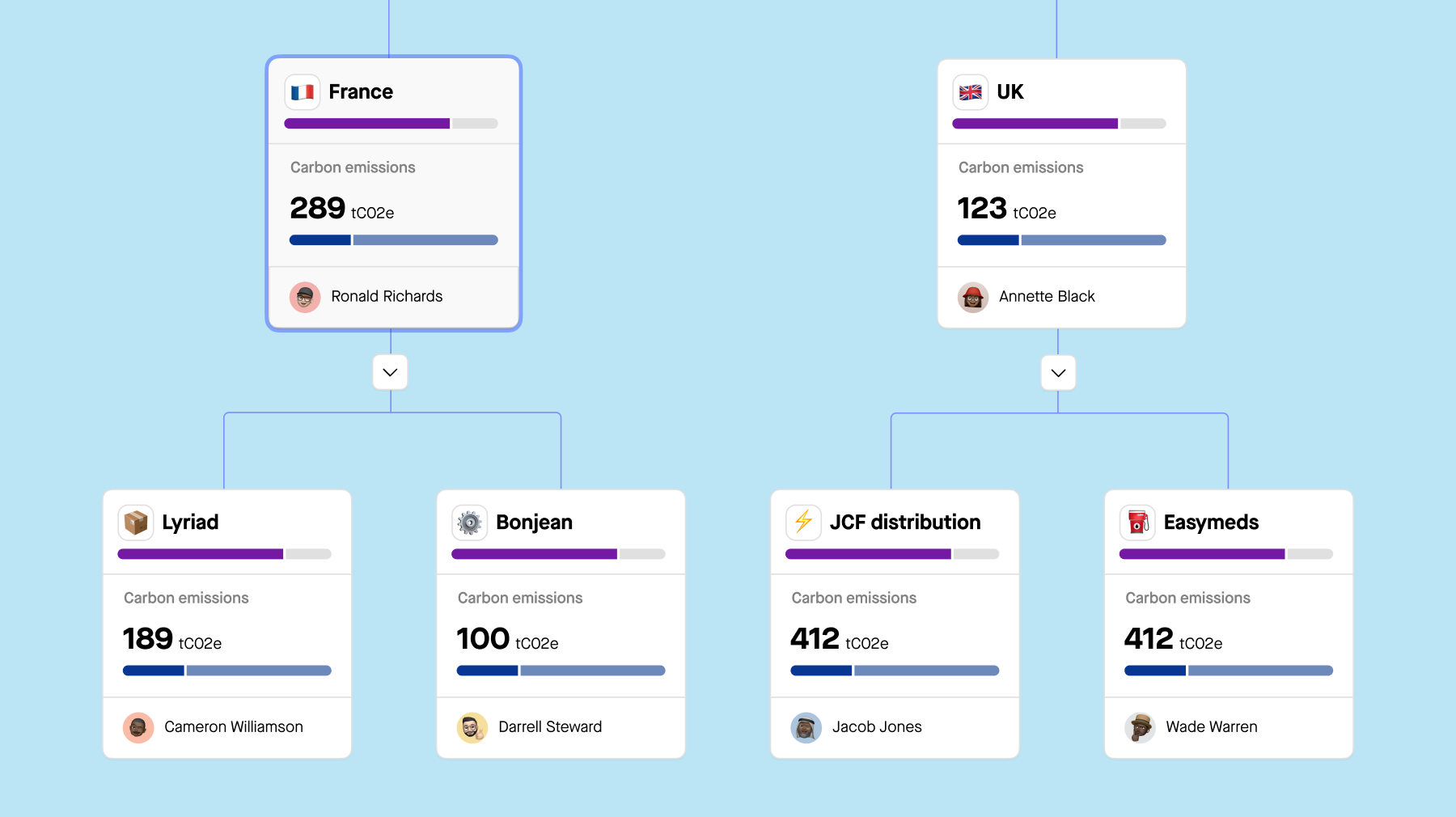
2. Selecting the right ESG audit standards and framework
Regardless of whether you're conducting an internal audit or engaging a third-party auditor, selecting the right ESG frameworks is essential. These frameworks should align with industry specifics and company objectives. They provide principles-based guidance for identifying ESG topics and structuring information and outline specific requirements for disclosing metrics.
Sweep can help you to:
-
Link corporate ESG indicators with standard disclosure requirements.
-
Utilize embedded standard indicators for efficient data collection.
-
Collect data once and use it for multiple standard disclosures.
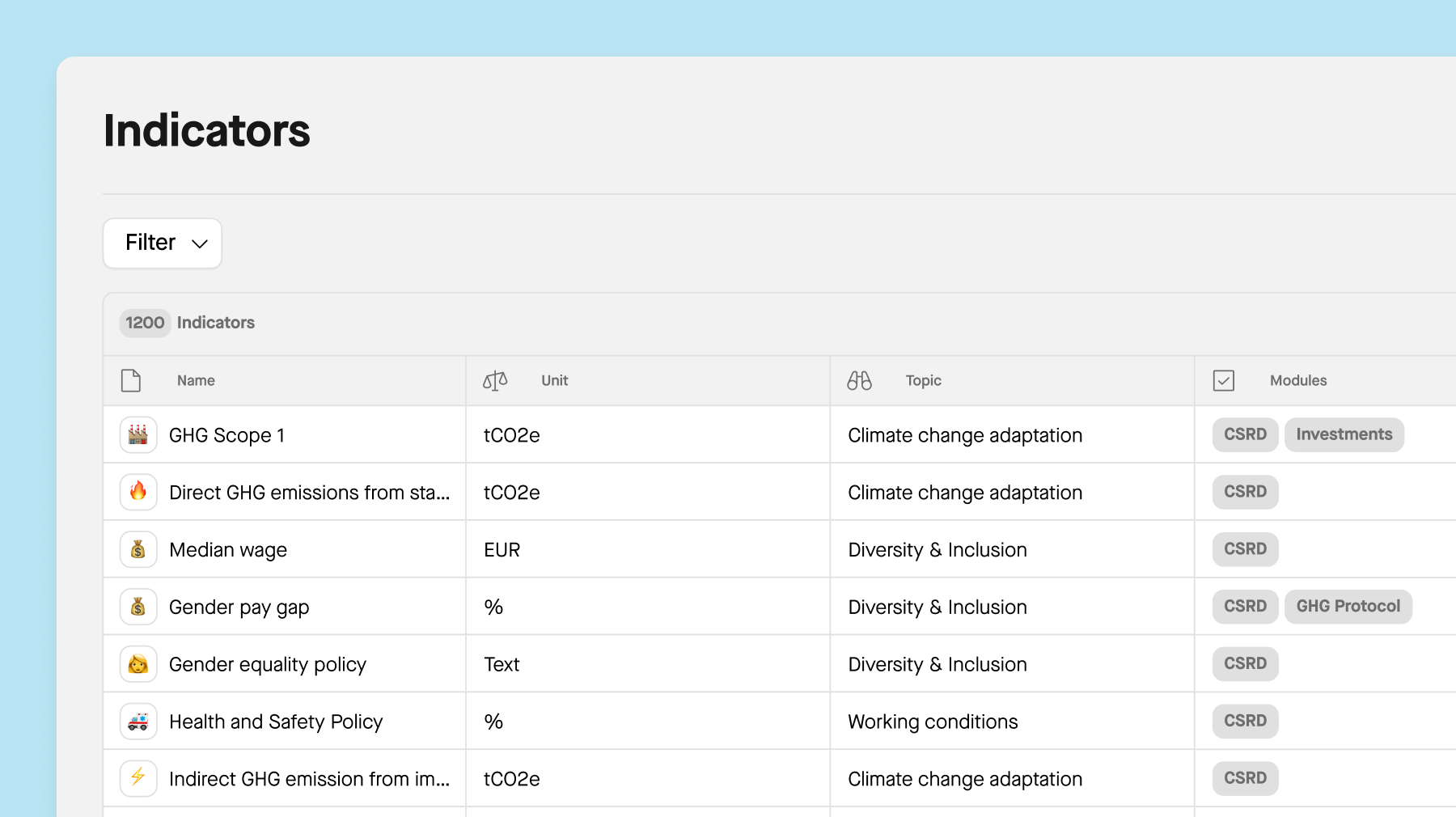
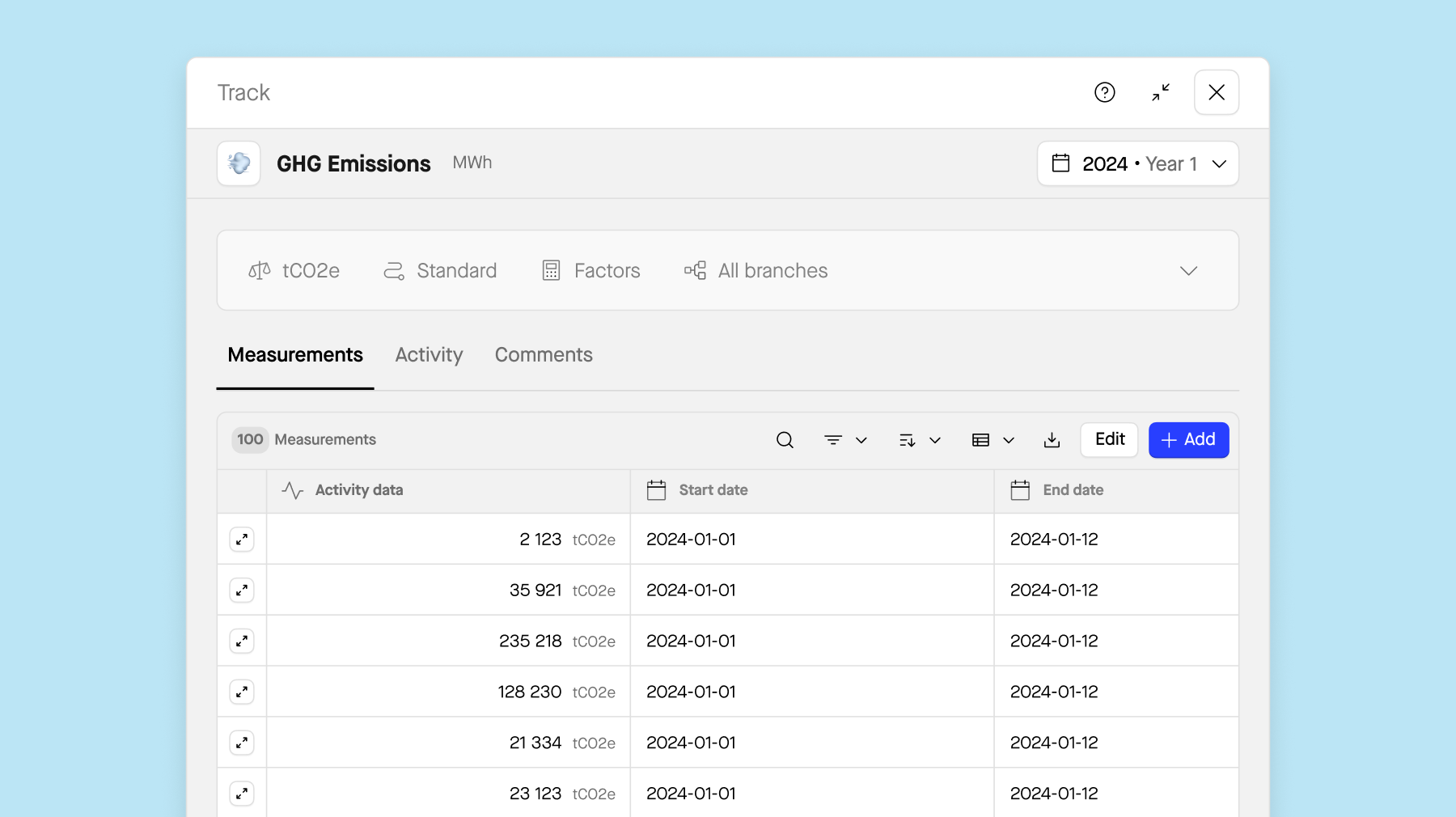
3. Collecting your data
Begin by collecting quantitative data, which forms the backbone of your audit. Based on the framework of your choice, this data may include metrics such as greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, water usage, waste generation, and diversity statistics. Quantitative data provides objective measurements of your organization's environmental and social performance. Additionally, review qualitative data such as ESG-related policies, procedures, and records within your organization. Conduct interviews with key personnel to gather insights into ESG practices and performance.
Sweep can help you to:
-
Collect data throughout the organization at the most granular level.
-
Time-stamp collected data for accuracy and accountability.
-
Track all changes and store document proofs securely.
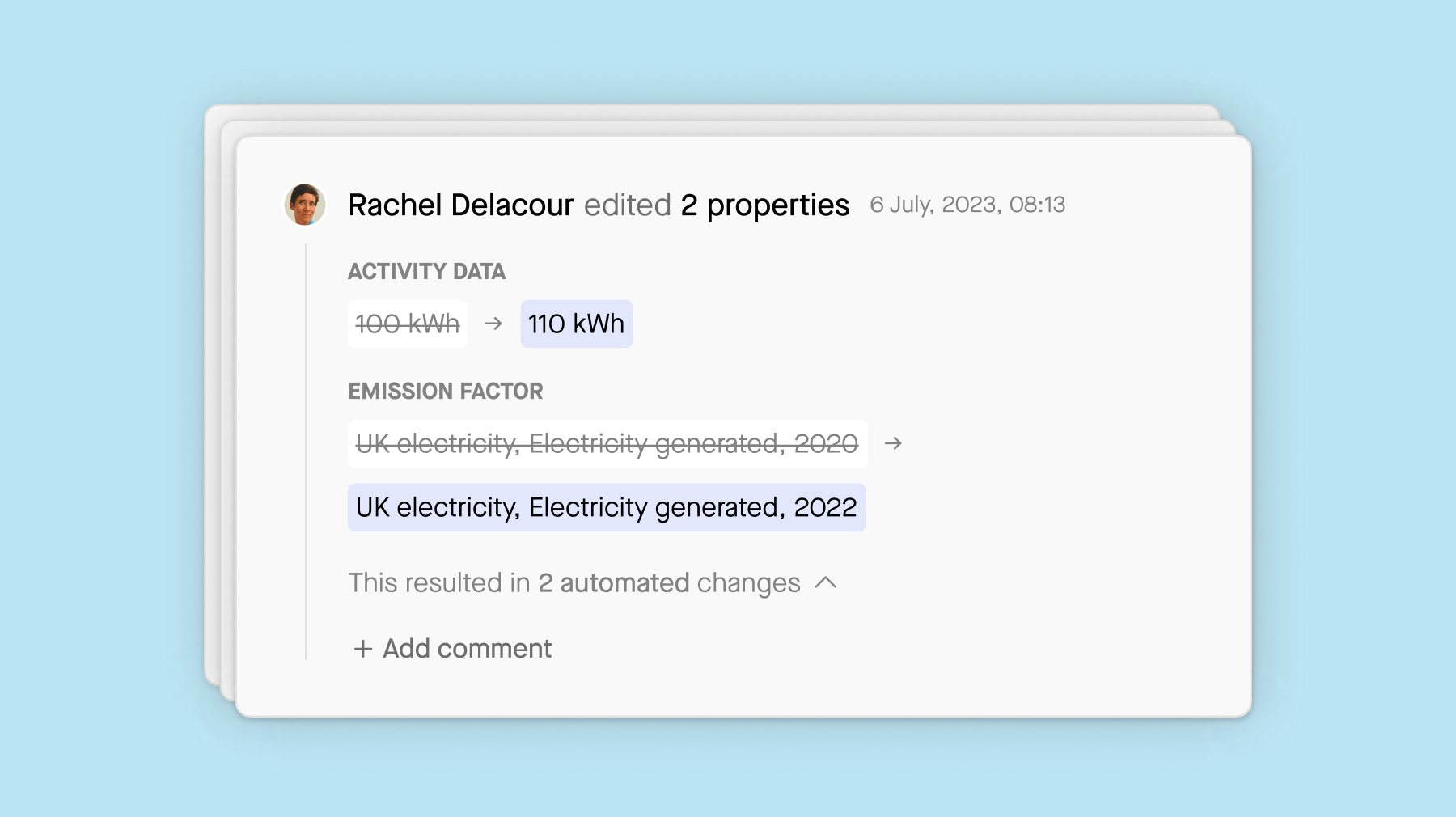
4. Creating an effective workflow for validation
Establishing an effective workflow for validation is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of ESG audit findings. This involves implementing robust processes to validate collected data, verify compliance with selected ESG frameworks, and ensure consistency across audit procedures. Creating clear guidelines and checkpoints for validation helps maintain quality standards throughout the audit process, ultimately enhancing the credibility of ESG reporting and audit outcomes.
Sweep can help you to:
-
Define a structured validation process for ensuring data reliability.
-
Validators can accept or reject responses and provide feedback.
-
Foster interaction between validators and contributors to enhance data quality.
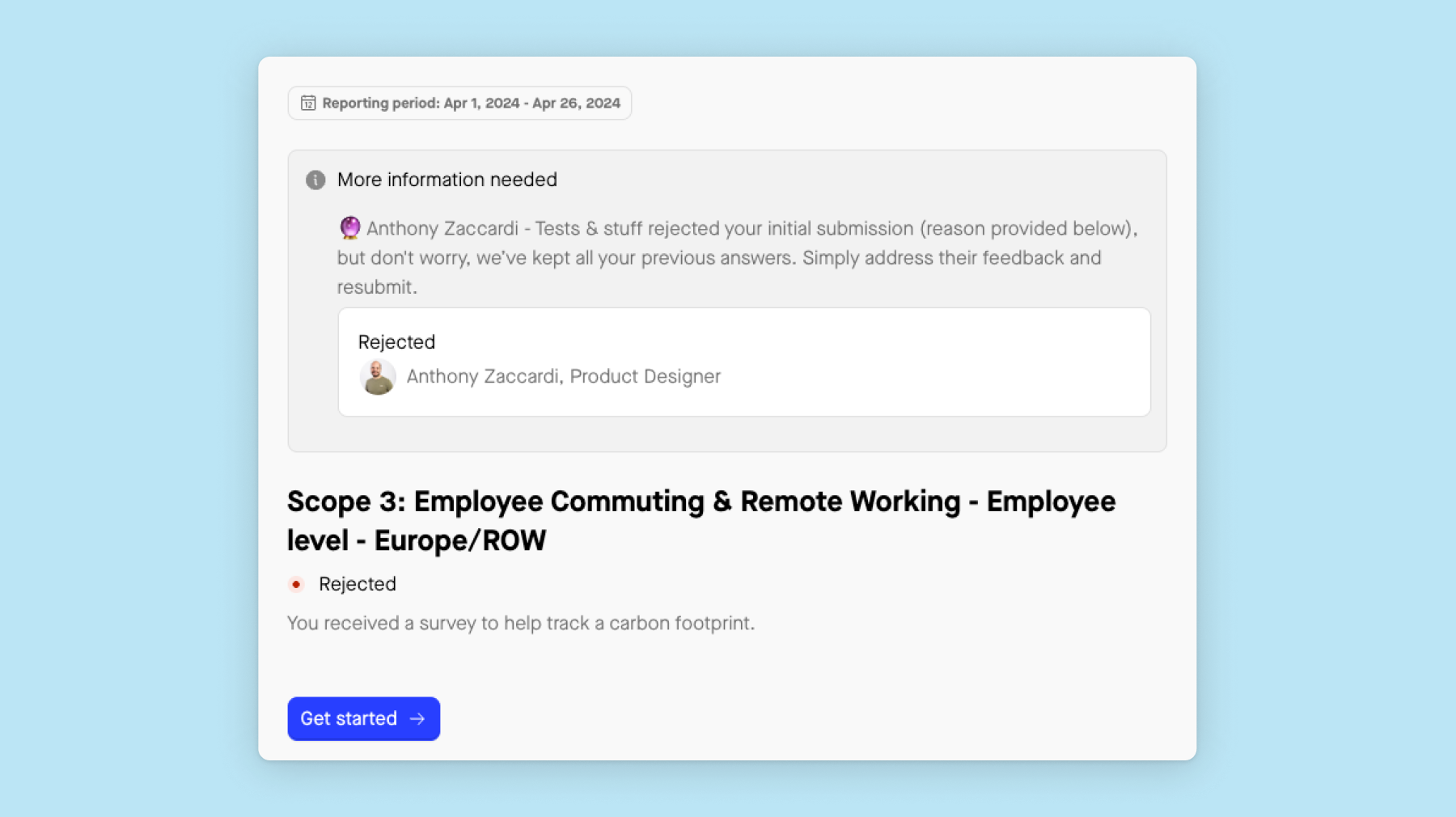
5. Preparing for ESG assurance engagements
Third-party assurance enhances ESG information reliability and stakeholder confidence. Auditors conduct attestation engagements to ensure ESG information aligns with specified criteria. Internal audit functions play a vital role in implementing standards consistently and establishing independent processes, given the current self-definition of ESG program requirements by most companies. ESG assurance engagements vary in scope, with a trend towards moving from limited to reasonable assurance. Companies often undergo assurance readiness assessments before engaging third-party auditors.
Sweep can help you to:
-
Select data samples for assessment with ease.
-
Assurance users can access requirement information for audit planning.
-
Utilize auditor profiles to streamline the audit process effectively.
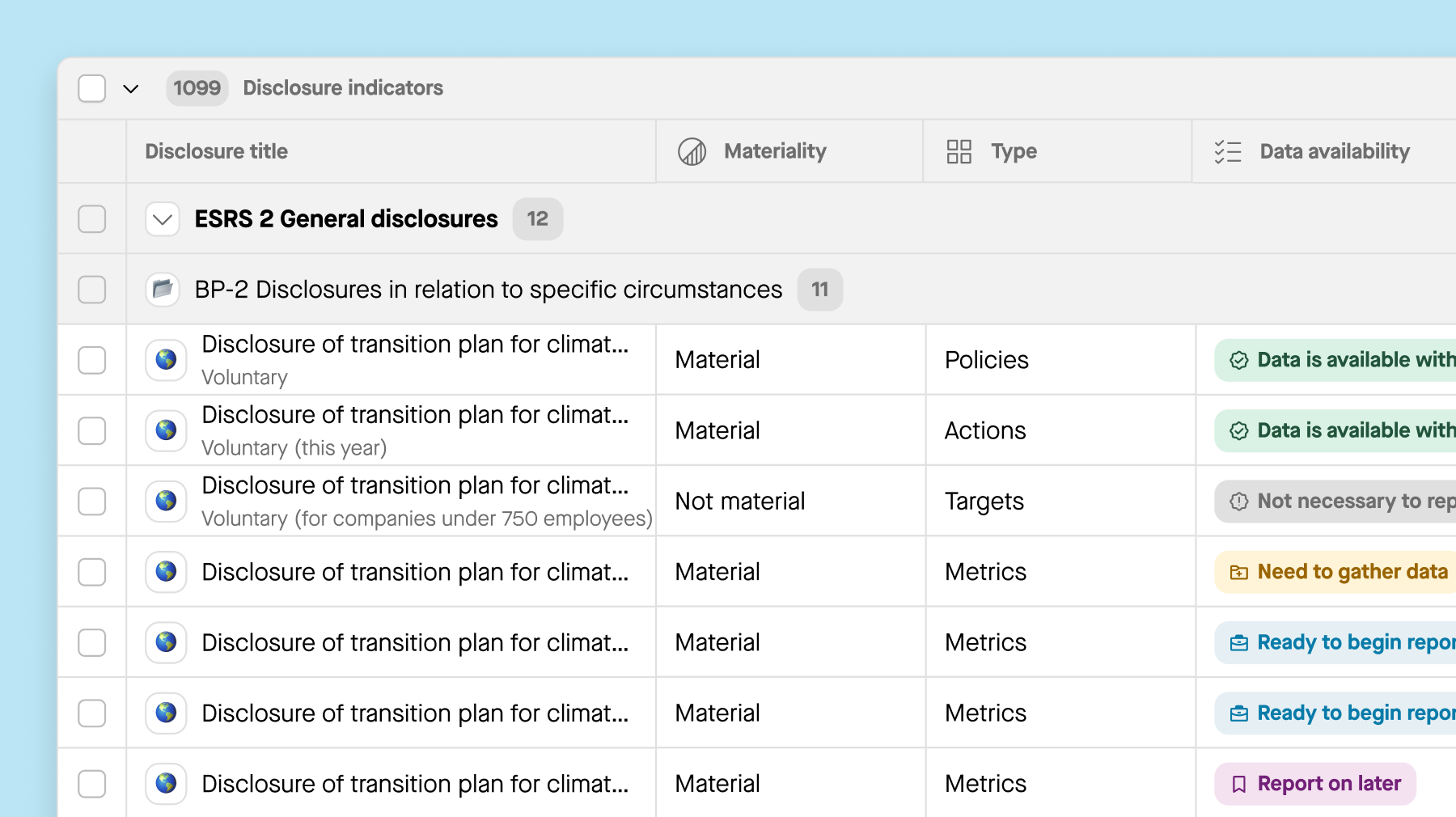
6. Integrating ESG into annual audit plans
ESG reporting is becoming increasingly important, necessitating its integration into annual audit plans. Regulations, such as SEC requirements for human capital resources reporting, are expected to evolve, particularly concerning climate-related disclosures in financial reporting. Integrating an annual ESG audit alongside traditional audit plans ensures reliable, transparent ESG information that meets the needs of stakeholders and regulatory entities consistently.
Sweep can help you to:
-
Assist external auditors in reviewing samples efficiently.
-
Utilize drill-down and drill-through functionalities for understanding data points.
-
Provide values and reasoning supported by document proofs for clarity and transparency.
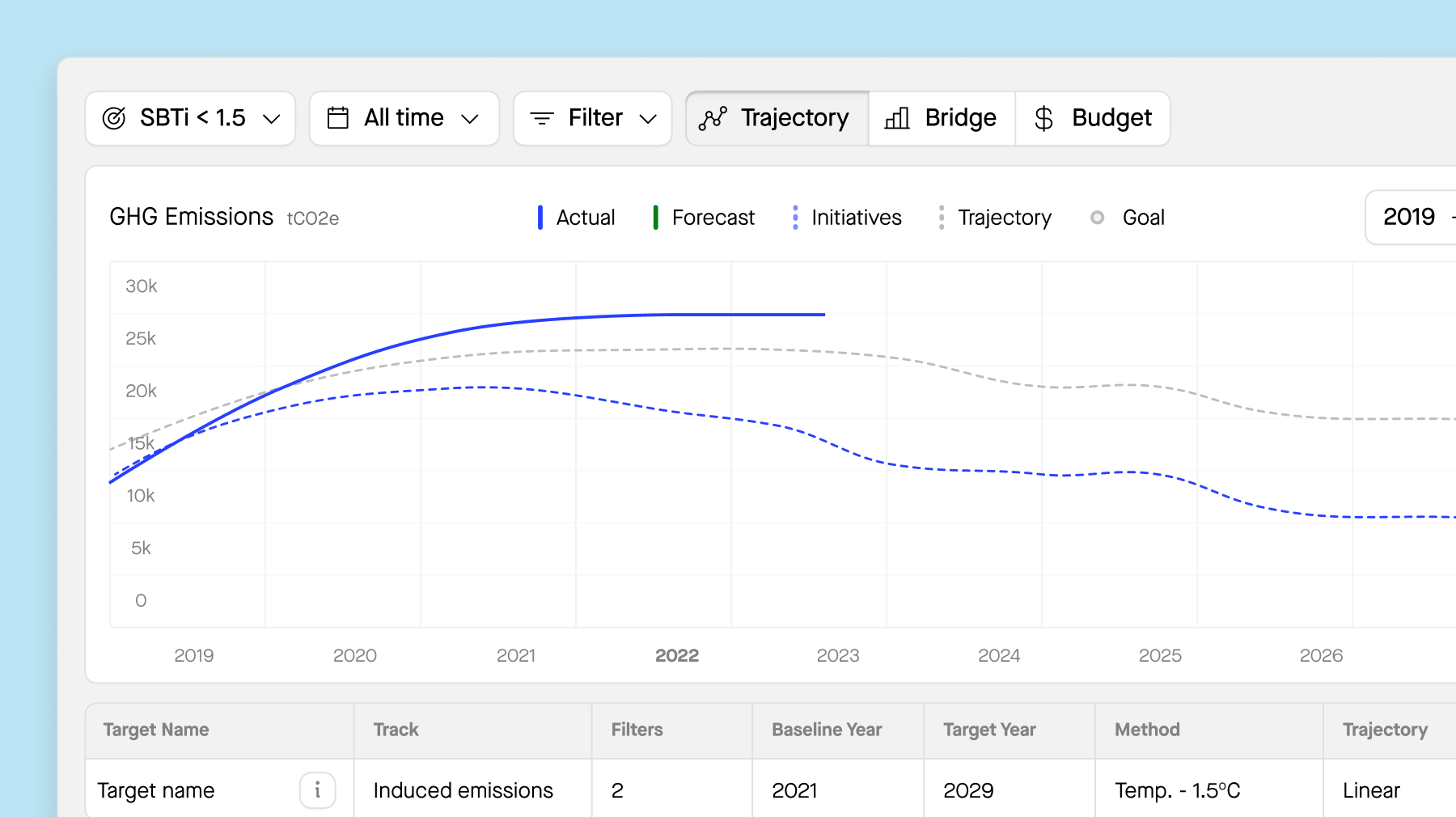
7. Follow-up and continuous improvement
The audit process doesn't end with the report. Follow up on recommended actions to ensure implementation. Conduct follow-up audits to monitor progress over time. By holding yourself accountable and tracking performance improvements, you can drive meaningful change and demonstrate your commitment to sustainability.
Sweep can help you to:
-
Launch action plans and initiatives seamlessly.
-
Define ownership, evaluate budgets, and track effectiveness.
-
Facilitate transition planning with clear steps and accountability.
Get started today
Book a demo with our team.