Climate change is one of the most pressing challenges of our time, driven by the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere. To address this issue effectively, scientists and policymakers rely on the metric of carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e). This measure is used to compare the emissions of various greenhouse gases by translating their warming effects into a standard unit relative to carbon dioxide (CO2).
Understanding Carbon Dioxide Equivalent (CO2e)

What is carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e)?
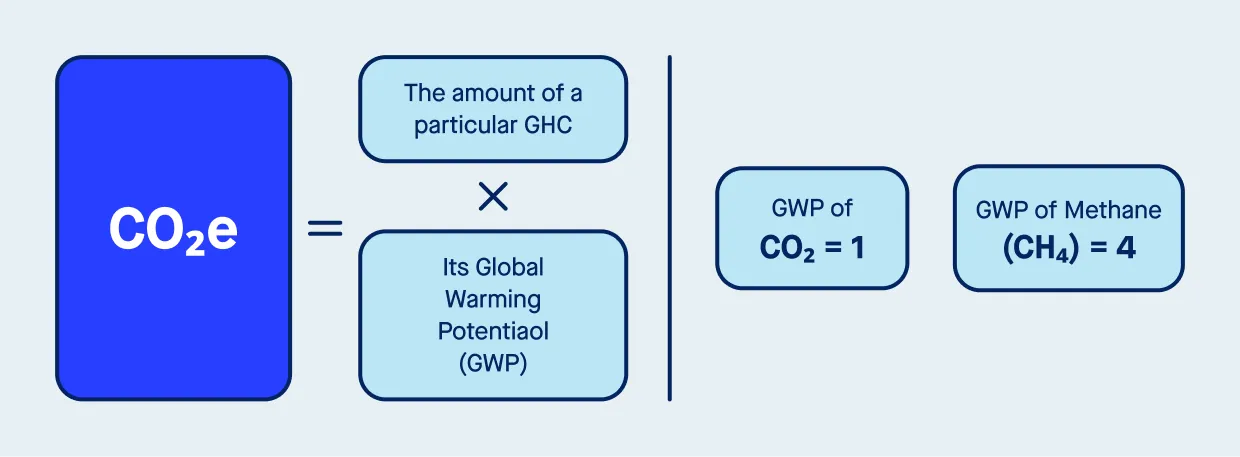
CO2e, or carbon dioxide equivalent, is a unit of measurement used to compare the impact of various greenhouse gases based on their contribution to global warming. Each greenhouse gas traps heat in the atmosphere differently, amplifying the greenhouse effect. This measure allows us to convert these differences into the same unit by converting amounts of other gases to the equivalent amount of carbon dioxide with the same global warming potential.
For example, methane (CH4) is much more potent than carbon dioxide, with a global warming potential (GWP) of approximately 28 times that of CO2 over 100 years. By converting methane’s impact into CO2e, we can assess its significance in relation to climate change mitigation.
This metric simplifies complex data into actionable insights, helping governments and organizations set emission reduction targets and track progress by accounting for carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. By expressing emissions in this way, decision-makers can identify the most impactful areas for intervention.
The origins of CO2e and the Kyoto Protocol
The concept of the carbon dioxide equivalent gained prominence with the 1997 Kyoto Protocol, an international treaty under the guidance of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The protocol established global standards for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and emphasized the importance of calculating emissions in a way that could be expressed relative to carbon dioxide. By creating a greenhouse gases based accounting system, the Kyoto Protocol laid the foundation for coordinated climate action.
Calculating CO2e
The calculation of CO2e involves multiplying the amount of a given greenhouse gas by its global warming potential. For example:
CO2e = (quantity of gas) × (GWP)
This calculation is crucial for understanding the total carbon emissions from various sources and their impact on global warming.
To calculate the equivalent of 1 metric ton of methane:
- Methane’s GWP = 28
- CO2e = 1 ton × 28 = 28 metric tons of CO2e
This means that emitting 1 metric ton of methane has the same warming effect as releasing 28 tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
The industrial revolution and its impact on emissions
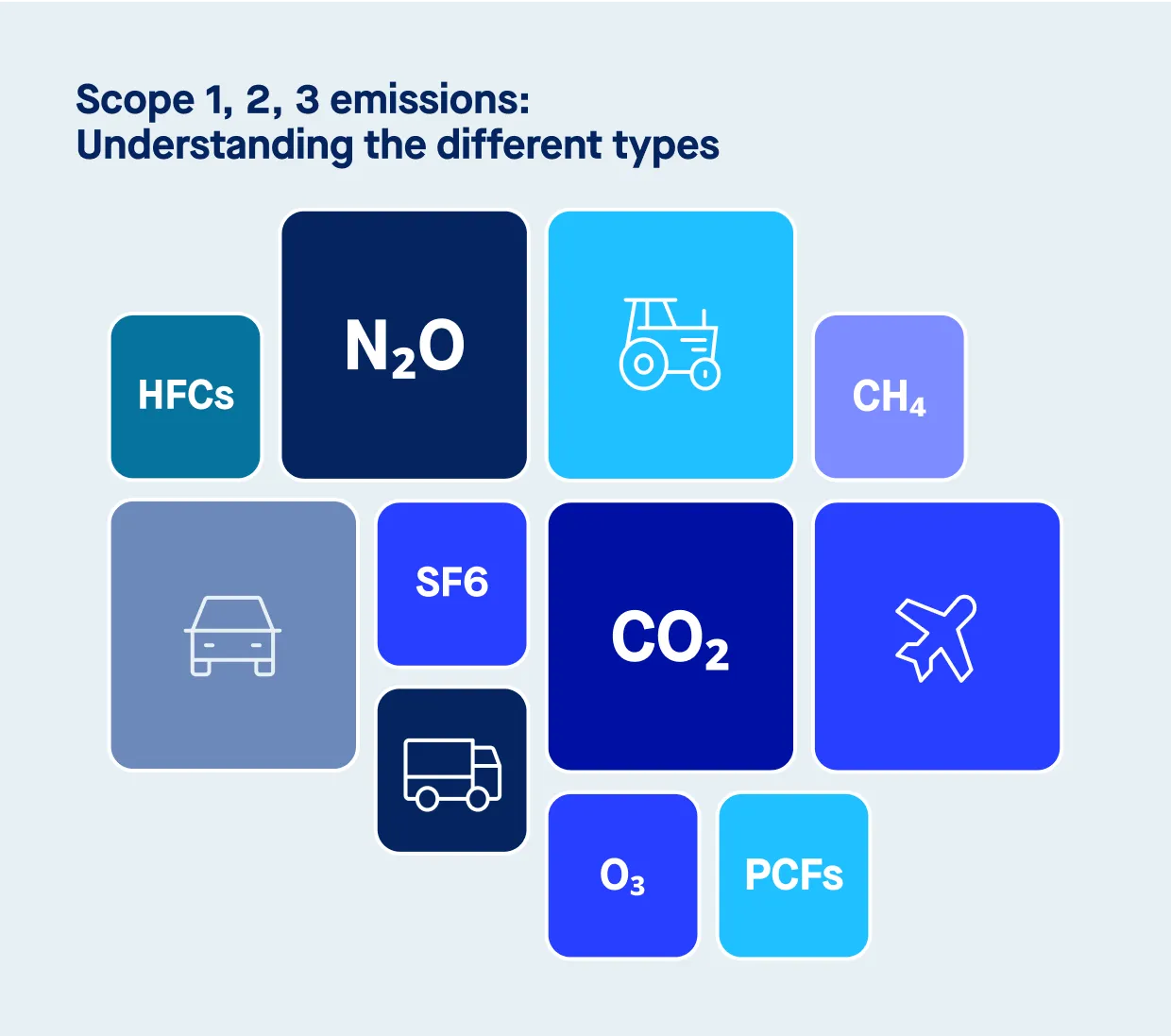
Since the industrial revolution, human activities have drastically increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The widespread use of fossil fuels, including natural gas, for energy, transportation, and industrial processes has led to rising emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), nitrogen trifluoride (NF3), water vapor, and perfluorocarbons (PFCs). These gases have intensified the greenhouse effect, resulting in global warming and rising temperatures.
Understanding the cumulative impact of these gases helps us trace the sources of emissions and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Applications of CO2e
The carbon dioxide equivalent is widely used across industries and policies to tackle climate change:
Carbon pricing: Carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems are often based on this measure, to determine the cost of emissions.
Carbon credits: Companies use it to quantify offset projects, such as reforestation or renewable energy investments.
Sustainability reporting: Businesses report their carbon footprint using this metric, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Climate research: Scientists use it to study the cumulative warming effects of greenhouse gases over time.
CO2e and energy efficiency
The concept of carbon dioxide equivalent is closely tied to carbon intensity, which measures the amount of carbon emissions per unit of energy produced. Lowering this intensity means producing energy more efficiently, resulting in fewer emissions for the same amount of energy. Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, play a crucial role in reducing emissions and their associated intensity.
Challenges in reducing emissions
Reducing emissions involves tackling diverse sources, including different greenhouse gases from energy production, transportation, agriculture, and industrial processes. Methane emissions from livestock, nitrous oxide from fertilizers, and SF6 from electrical equipment are particularly challenging to address. However, innovations in technology and shifts toward sustainable practices offer pathways to overcome these challenges.
The role of carbon management platforms
Carbon management platforms are increasingly essential in the global effort to reduce emissions. These platforms use advanced data analytics to monitor and manage emissions from various sources, making greenhouse gases comparable and easier to track. By integrating data from energy use, industrial processes, and transportation, these tools enable organizations to identify high-emission areas and implement targeted reductions.
Furthermore, carbon management platforms simplify the process of calculating emissions from other gases, ensuring that all contributions to global warming are accounted for. They also help companies adhere to sustainability standards, meet regulatory requirements, and participate in carbon credit markets.
Moving toward a sustainable future
The carbon dioxide equivalent is a crucial metric for understanding and addressing the complexities of climate change. By expressing emissions in a comparable way, it enables policymakers, industries, and individuals to take targeted action.
As we face rising temperatures and increasing environmental challenges, reducing emissions is essential. The adoption of carbon management platforms and innovative strategies for emissions reduction will help us move toward a more sustainable and resilient future.
Sweep can help
Sweep is a carbon and ESG management platform that empowers businesses to meet their sustainability goals.
Using our platform, you can:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of your carbon footprint.
- Get a real-time overview of your supply chain and ensure that your suppliers meet your sustainability targets.
- Reach full compliance with the CSRD and other key ESG legislation in a matter of weeks.
- Ensure your sustainability information is reliable by having it verified by a third party before going public.