As businesses increasingly recognize their broader impact on society and the environment, concepts like Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) have gained prominence. These frameworks encourage businesses to operate in ways that go beyond profit generation and integrate socially responsible business practices into their operations. However, while both CSR and ESG focus on sustainability and ethical responsibility, they differ in their application, measurement, and objectives.
Understanding these distinctions is vital for businesses seeking to align their corporate values with the expectations of stakeholders, customers, and regulators. In this post, we will explore the concept of CSR, break down its different types, and clarify how it differs from ESG, ultimately showing how each plays a key role in driving competitive advantage, fostering stronger relationships with local communities, and ensuring long-term sustainability.
Defining Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
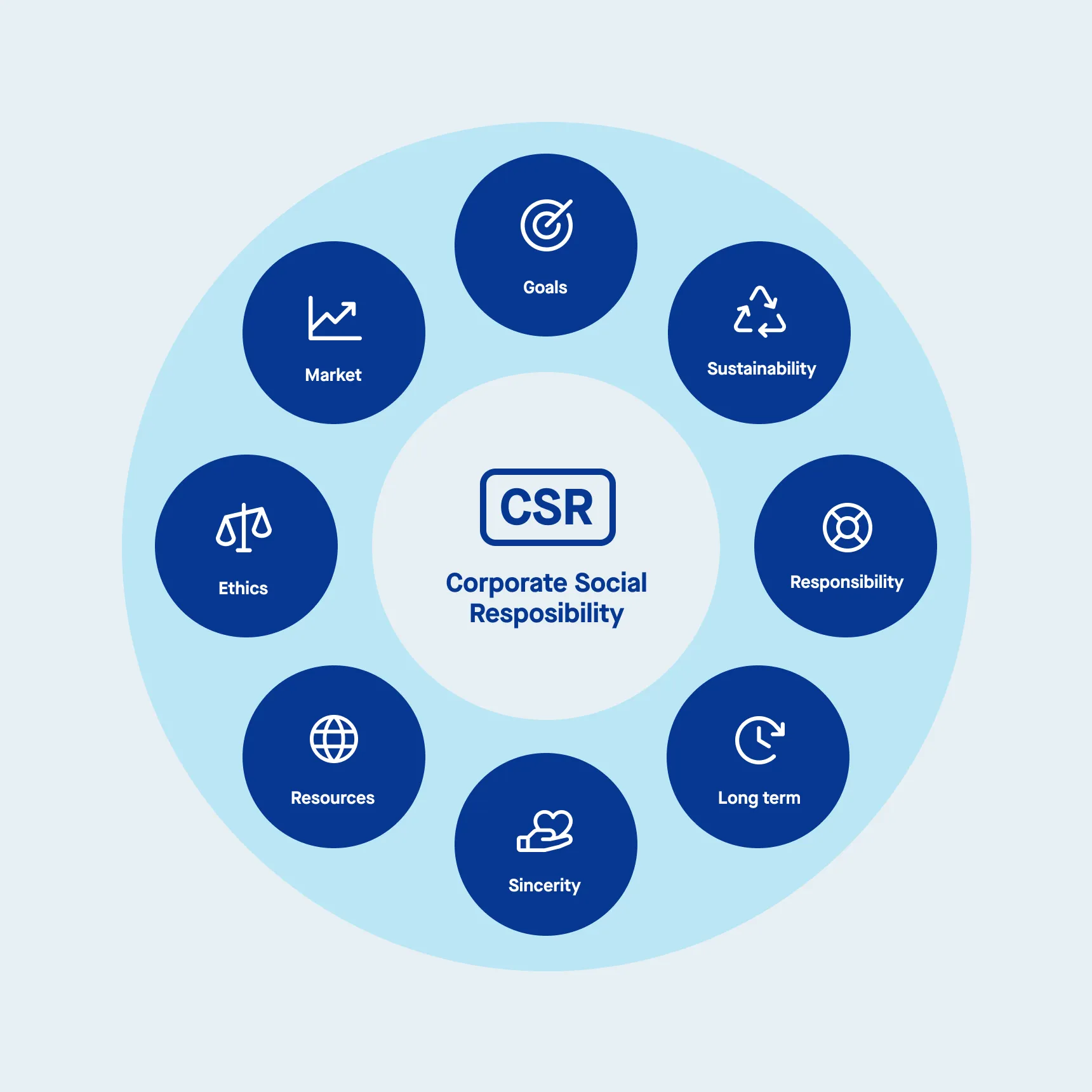
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a business model that encourages companies to integrate social and environmental concerns into their business operations and decision-making processes. At its core, CSR reflects the belief that businesses should not focus solely on financial performance but should also contribute to societal goals that promote environmental protection, fair labor practices, and community engagement. Companies actively practicing corporate social responsibility can positively influence economic, social, and environmental aspects. This approach aligns corporate values with the well-being of broader stakeholder groups, including employees, customers, investors, and the local community.
Companies engaging in CSR initiatives often do so voluntarily, taking on socially responsible business practices as part of their broader strategy to enhance reputation, strengthen customer loyalty, and foster positive relationships with employees and society. In many cases, CSR can act as both a form of corporate accountability and a strategic marketing scheme, allowing businesses to demonstrate their commitment to ethical behavior and community welfare.
CSR differs from concepts like corporate accountability, which focuses more narrowly on a company’s obligation to be transparent and answerable for its actions. Corporate sustainability, another related term, extends beyond CSR by embedding sustainability into the company’s core business model with the goal of balancing profit, people, and the planet over the long term.
The different types of CSR: A comprehensive breakdown
CSR practices and initiatives come in many forms, generally categorized into four key areas: environmental responsibility, ethical responsibility, philanthropic responsibility, and financial responsibility. Each type contributes to how businesses manage their social impact while driving a positive outcome for society and the environment.
1. Environmental responsibility
Environmental responsibility is a core element of CSR and reflects a company’s commitment to reducing its environmental impact. This can include actions aimed at minimizing resource consumption, cutting down greenhouse gas emissions, adopting renewable energy sources, and promoting sustainable business practices. Companies may also implement environmentally conscious supply chains, ensuring that their products and services are sourced and manufactured in ways that minimize harm to the environment.
For example, many businesses have taken steps to reduce plastic usage, introduce energy-efficient production processes, or support reforestation initiatives. These efforts not only help protect the planet but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, giving the company a competitive advantage in increasingly eco-aware markets.
2. Ethical responsibility
Ethical responsibility in CSR refers to a company’s obligation to conduct business in a way that is fair and just. This includes treating employees and suppliers ethically, ensuring fair wages, promoting diversity, and safeguarding human rights within the company’s operations and supply chains. Businesses committed to ethical CSR initiatives often go beyond legal compliance, striving to maintain high ethical standards in their relationships with stakeholders.
For example, companies may adopt policies that prevent labor exploitation, ensure gender and ethnic diversity within employee groups, and provide fair working conditions across all levels of their business operations. These practices not only foster loyalty among employees and customers but also enhance a company’s public image as a responsible and trustworthy business entity.
3. Philanthropic responsibility
Philanthropic CSR involves contributing to the welfare of society through charitable donations, community service, and other forms of support for social causes. Companies may allocate a portion of their profits to non-profits or partner with local organizations to fund projects that benefit the local community. This type of CSR is often seen in companies that sponsor educational programs, support healthcare initiatives, or provide relief during natural disasters.
Unlike other forms of CSR, philanthropic responsibility may not directly improve the company’s profitability, but it serves to strengthen the company’s relationship with the community, boost its reputation, and foster goodwill. Many businesses create corporate foundations to manage their philanthropic efforts, ensuring alignment with their corporate values and long-term social impact goals.
4. Financial responsibility
Financial responsibility refers to the way businesses manage their financial investments while taking into account their social and environmental impacts. In this context, businesses seek to balance profit generation with responsible financial behavior. This could involve supporting responsible investment initiatives, avoiding industries like fossil fuels or tobacco, and prioritizing investments in sustainable technologies or social enterprises.
Financial responsibility also ties into transparent financial reporting, ensuring that a company’s economic practices align with its broader CSR strategy. Companies that adopt sustainable financial practices often find that they can improve their long-term viability, attract socially conscious investors, and reduce their exposure to financial risks associated with unethical or unsustainable operations.
ISO 26000: A framework for social responsibility
ISO 26000 is an international standard that provides guidance on how businesses can integrate social responsibility into their operations. Unlike other ISO standards, ISO 26000 is not certifiable; instead, it offers voluntary guidelines that companies can follow to enhance their CSR strategies. This standard covers a wide range of topics, including human rights, labor practices, the environment, consumer issues, and community involvement.
Adopting ISO 26000 helps businesses ensure that they operate in a socially responsible manner while enhancing their credibility and improving their competitive advantage. By following these guidelines, companies can better align their operations with stakeholder expectations, create a positive social impact, and build stronger relationships with the local community.
CSR initiatives and examples
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives are essential for companies aiming to make a positive impact on society and the environment. These initiatives not only enhance a company’s reputation but also contribute to its long-term success. Here are a few examples of successful CSR initiatives that have made a significant difference:
Successful CSR Initiatives
- Environmental sustainability: Companies like Patagonia and REI have set the bar high with their environmental sustainability initiatives. Patagonia, for instance, uses recycled materials in its products and actively supports reforestation projects. REI promotes sustainable supply chains and encourages customers to reduce waste through its “Opt Outside” campaign. These efforts not only help protect the planet but also resonate with environmentally conscious consumers, giving these companies a competitive advantage.
- Community development: Ben & Jerry’s and The Body Shop are renowned for their community development initiatives. Ben & Jerry’s supports local charities and promotes fair trade practices, ensuring that their ingredients are sourced ethically. The Body Shop has implemented job training programs and supports various social causes, such as human rights and animal welfare. These initiatives strengthen their relationship with the community and enhance their brand value.
- Employee engagement: Tech giants like Google and Facebook have excelled in employee engagement initiatives. Google offers volunteer days and professional development opportunities, fostering a culture of giving back and continuous learning. Facebook promotes diversity and inclusion through various programs and initiatives, ensuring a supportive and inclusive workplace. These practices not only boost employee morale but also attract top talent, contributing to the company’s overall success.
These CSR initiatives demonstrate how companies can integrate socially responsible business practices into their operations, benefiting both society and their business.
Implementing CSR Strategies
Developing a comprehensive CSR strategy is crucial for companies aiming to make a meaningful impact. A well-thought-out CSR strategy aligns with the company’s mission and values, ensuring that CSR efforts are effective and sustainable. Here are some steps to consider when developing a CSR strategy:
Developing a CSR Strategy
- Conduct a stakeholder analysis: Identify key stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors, and community members. Understanding their needs and expectations is essential for developing relevant CSR initiatives.
- Assess business operations: Evaluate your business operations to identify areas for improvement and opportunities for CSR initiatives. This assessment helps pinpoint where your company can make the most significant impact.
- Set CSR goals and objectives: Establish clear CSR goals and objectives that align with your company’s mission and values. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Develop a CSR plan: Create a comprehensive CSR plan that outlines initiatives, timelines, and budgets. This plan should detail how each initiative will be implemented and monitored.
- Implement and monitor CSR initiatives: Put your CSR initiatives into action and regularly monitor their progress. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of your initiatives and make adjustments as needed.
By following these steps, companies can develop a CSR strategy that not only enhances their corporate responsibility but also drives business success and creates a positive impact on society.
CSR certifications and standards
CSR certifications and standards play a vital role in demonstrating a company’s commitment to social responsibility and sustainability. Obtaining these certifications can differentiate a company from its competitors and enhance its credibility. Here are two notable examples:
B-Corp certification and ISEAL code compliance
- B-Corp certification: B-Corp certification is a rigorous and holistic verification process that requires companies to meet high standards of social and environmental performance, accountability, and transparency. Companies like Patagonia and Ben & Jerry’s are certified B-Corps, showcasing their commitment to being socially responsible businesses. The certification process involves a comprehensive assessment of a company’s impact on its workers, customers, community, and environment.
- ISEAL code compliance: ISEAL code compliance is a third-party verification process that requires companies to meet Codes of Good Practice and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. This certification ensures that companies adhere to high standards of ethical responsibility and environmental stewardship. By achieving ISEAL code compliance, companies can enhance their reputation and build trust with stakeholders.
By obtaining these certifications, companies can demonstrate their commitment to corporate social responsibility and sustainability, positioning themselves as leaders in ethical business practices and corporate citizenship.
The benefits of having a CSR strategy
Having a comprehensive CSR strategy can yield numerous benefits for businesses, ranging from improved brand reputation to better financial performance. Being recognized as a socially responsible company can significantly attract and retain top talent, especially among younger generations who value community engagement and ethical practices. Below are some of the key advantages of integrating CSR initiatives into a company’s business model.
1. Improved reputation and customer loyalty
In today’s marketplace, customers are increasingly drawn to companies that practice socially responsible business practices. A strong CSR strategy signals that a company cares about more than just profits, which can enhance brand loyalty and customer retention. Companies with a reputation for positive social and environmental impact are often better positioned to differentiate themselves from competitors and attract a loyal customer base.
2. Employee engagement and talent attraction
A robust CSR strategy can also lead to higher employee engagement and help attract top talent. Employees are more likely to stay with companies that align with their personal values, especially in areas related to environmental responsibility and social impact. In addition, businesses with a clear commitment to ethical practices and community involvement tend to foster greater employee morale and job satisfaction, reducing turnover rates and enhancing productivity.
3. Operational efficiency and cost savings
Many CSR initiatives lead to improved operational efficiencies and cost savings. For example, businesses that adopt energy-efficient technologies or streamline their supply chains to reduce waste can often see lower operating costs over time. Additionally, companies that implement sustainable resource management practices, such as water conservation or waste reduction, contribute to long-term environmental stewardship while boosting their profitability.
4. Risk management and regulatory compliance
CSR initiatives can help companies mitigate risks associated with unethical practices or environmental degradation. Businesses that proactively address environmental and social concerns are better positioned to comply with regulatory requirements and avoid costly fines or legal action. CSR can also serve as a buffer against reputational damage, ensuring that the company maintains a positive public image even in times of crisis.
5. Increased investor confidence
Many investors today are looking for companies with strong CSR strategies and ESG performance. By demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and ethical governance, businesses can attract socially conscious investors and gain access to capital markets that prioritize responsible financial investments. A focus on CSR not only enhances investor confidence but also strengthens long-term financial performance.
What is ESG, and how does it differ from CSR?
While CSR and ESG share a common goal of promoting sustainability and ethical business practices, they differ in several important ways, particularly in terms of focus and measurement.
What is ESG?
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. Unlike CSR, which is often a broad, voluntary approach to social responsibility, ESG refers to specific criteria used by investors to assess a company’s sustainability and ethical performance. ESG factors are used to evaluate how well a company manages risks and opportunities related to environmental sustainability, social impact, and governance structures. These factors play a crucial role in shaping financial investments, as more investors seek to integrate sustainability into their decision-making processes.
Key differences between CSR and ESG
- Scope and focus
- CSR tends to focus on a company’s internal commitment to socially responsible business practices. It is often viewed as a voluntary set of actions that a company takes to enhance its social and environmental impact.
- ESG is more externally focused, particularly in its relevance to investors and regulators. ESG criteria provide measurable data points that allow stakeholders to assess a company’s performance in areas like carbon emissions, diversity, board governance, and supply chain management.
- Measurement and accountability
- CSR initiatives are often qualitative and focus on improving a company’s reputation through social impact initiatives, community engagement, and ethical behavior.
- ESG metrics, by contrast, are quantitative and provide standardized measures that are used by investors to assess a company’s sustainability performance. These metrics can be tracked and reported, allowing for greater transparency and accountability.
- Investor focus
- While CSR tends to prioritize stakeholder engagement and brand loyalty, ESG is primarily a tool for evaluating the long-term viability of a company’s business model from an investment perspective. Investors use ESG factors to determine whether a company is well-positioned to navigate future risks and capitalize on sustainability opportunities.Cor
A holistic approach: CSR and ESG as complementary forces
Both CSR and ESG play vital roles in shaping a sustainable and socially responsible future. CSR enables companies to demonstrate their commitment to ethical business practices, local community support, and environmental stewardship. It fosters goodwill, strengthens customer loyalty, and engages employee groups in ways that enhance corporate values.
On the other hand, ESG provides a structured, data-driven framework that allows companies to measure and report their environmental, social, and governance impact in a transparent manner. Investors increasingly rely on ESG metrics to assess the sustainability of their financial investments, making it a crucial consideration for businesses seeking to secure long-term success.
Together, CSR and ESG form a powerful strategy that helps companies not only improve their social and environmental impact but also drive long-term profitability, reduce risks, and build lasting relationships with stakeholders. By integrating both CSR and ESG into their business operations, companies can align their business model with global sustainability goals while positioning themselves as leaders in ethical business practice.