We give you a useful overview of the two main sustainability disclosure regulations in the UK and EU, who they affect and the key differences between them.
What are the SDR and the SFDR?
The UK Sustainable Disclosure Regulation (SDR) and EU Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) are both sustainability disclosure regulations for financial market participants.
-
The UK SDR, led by the UK Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), aims to provide investors with more comprehensive, consistent and comparable sustainability information from issuers and investment managers.
The regulation applies to issuers of bonds and shares listed on a UK regulated market and UK-based investment managers.
-
The EU SFDR, led by the European Commission, sets out sustainability-related disclosure requirements for financial market participants such as investment firms, insurance and reinsurance companies.
The SFDR applies to entities established in the EU and extends to products marketed in the EU, regardless of the location of the entity.
So the UK SDR only applies to UK-based companies, while EU SFDR applies to EU-based companies and entities marketing products in the EU. There will then be a significant number of firms who need to consider the applicability of both the UK and EU requirements.
What are the objectives of these regulations?
Both the UK SDR and EU SFDR are designed to:
-
build trust and integrity in sustainable instruments to fight greenwashing
-
increase transparency and disclosure around sustainable finance products and investments
-
give investors more information to make informed investment decisions.
What are the main differences between SDR and SFDR?
Although the SDR is generally considered to be the UK’s answer to the EU’s SFDR, the two regimes are far from being aligned. Below, we outline some of the major differences.
1. Sustainable investment classification and labels
The objective here is to address greenwashing. The FCA is clamping down on “exaggerated, misleading or unsubstantiated claims” regarding sustainable investment products.
Consumer-facing disclosures are meant to help investors understand the key sustainability-related features of an investment product.
🔍The UK SDR proposed three labels (focus, impact, improve) and these don't correspond to the three categories in SFDR (Article 6, 8 and 9).
a) SDR
Under SDR, financial products will be labelled based on intentionality and on the level of sustainable investments. SDR offers more clarity to funds in determining their appropriate label and potentially will offer investors more certainty in selecting funds that reflect their preferences.

The three labels are designed to not have a hierarchy and instead reflect the desires of different consumer preferences, as outlined below:
-
Sustainable Focus – Assets that mainly have an environmentally or socially sustainable focus.
This label suggests that the fund maintains a high standard of sustainability in the profile of the assets (It should invest at least 70% in sustainable assets, as suggested in the consultation paper).
-
Sustainable Improvers – Assets that may not be sustainable now, but are aiming to have a positive environmental or social impact in the future.
This label is the most novel and brings the idea of “stewardship” on the part of the asset manager to make a “measurable” improvement in underlying ESG performance.
-
Sustainable Impact – Assets that invest in real-world problems and are achieving real-world measurable contributions to environmentally or socially sustainable outcomes.
This label includes products with a specific sustainable outcome as an objective, with no minimum sustainable investment required.
b) SFDR
According to the SFDR’s classification system, a fund will either be classified as an article 6,8 or 9 fund – depending on their characteristics and level of sustainability. The SFDR categories are not labels and instead represent levels of disclosures that the fund will make.
-
Article 6: Funds without a sustainability scope
-
Article 8: Funds that promote environmental or social characteristics
-
Article 9: Funds that have sustainable investment as their objective
|
SFDR Classification |
Description |
Alignment with SDR |
|---|---|---|
|
Article 6 |
Funds that do not integrate sustainability into their investment process. |
Does not meet the criteria to achieve a label. |
|
Article 8 |
Funds that promote sustainable investment, but it is not a primary objective. |
Sustainable Focus and Sustainable Improver funds would exceed the criteria for Article 8. |
|
Article 9 |
Funds that have sustainable investment as a primary objective. |
Sustainable Impact funds would exceed the criteria for Article 9. |
The FCA labels cover different investment objectives, whereas the three SFDR categories do suggest a hierarchy of sustainability. There is a minimum set of criteria for each SDR label (unlike SFDR): e.g. for a “focus” fund, they must commit to invest at least 70% in sustainable assets.
The FCA, acknowledging that firms may already have implemented SFDR, shows how one can map to the other in its consultation paper.
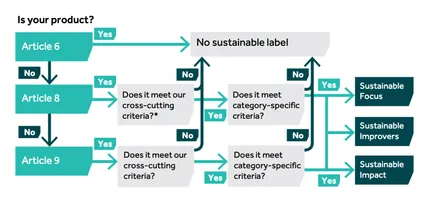
As you seen it’s not that obvious! A firm could have an investment product that is categorised as Article 8 or 9 under the SFDR but does not meet the qualifying criteria for the investment labels within the SDR. This could cause confusion in the market where a product is seen as sustainable according to one regime but not to another.
2. Sustainability Disclosures
The UK proposal differs from SFDR on determining whether investments are sustainable or not:
-
The SDR doesn’t contain a “do no significant harm” test. This may be introduced at a later stage, but for now the FCA views it as too restrictive.
-
The SDR also doesn’t include any reference to Taxonomy alignment. We expect this to change when the UK Taxonomy is developed.
-
The SDR doesn’t have any reference to the reporting of Principal Adverse Impact indicators (PAIs).
🔍 FCA will look to develop quantitative KPI disclosures based on, amongst other things, TCFD and ISSB standards.
The key differences in a nutshell
|
Firms making SFDR product-level disclosures will be considering… |
Is this required under SDR proposals? |
|---|---|
|
Sustainable investment objective; E or S characteristics of the product |
Yes – Principle 1: sustainability objective |
|
Monitoring sustainability objective; E or S characteristics (sustainability indicators) |
Yes – Principle 3: KPIs |
|
DNSH |
No |
|
Principal adverse impacts |
No |
|
Investment strategy |
Yes – Principle 2: investment policy and strategy |
|
Asset allocation/proportion of investments that promote E or S characteristics (including use of derivatives) |
Yes – Principle 2: investment policy and strategy |
|
Taxonomy-alignment |
No |
|
Methodologies, data sources and processing, limitations to methodologies and data |
Yes – Part B sustainability product report |
|
Due diligence |
Yes – Principle 4: governance and resources |
|
Engagement policies (where part of strategy) |
Yes – Principle 5: stewardship |
|
Reference benchmarks |
Yes – Principle 2: investment policy and strategy |
|
Extent to which E or S characteristics/sustainable investment objective were met (performance of sustainability indicators) |
Yes – Principle 3: KPIs |
|
Proportions of investments (eg top investments; those that attained E or S characteristics/met the objective; those in different economic sectors and sub-sectors; Taxonomy-aligned) |
No |
|
Performance against designated reference benchmark |
Yes – Principle 3: KPIs (eg where a benchmark has been designated as a performance indicator) |
|
Historical comparison |
Yes – Part B sustainability product report |
|
Information on underlying investment options |
No |
When will the SDR come into place?
The UK SDR will come into effect twelve months after the publication of the final rules. These are expected in the first half of 2023, along with clarifications on greenwashing in the form of a policy statement.
However, the clarification on greenwashing will come into effect immediately. Funds that currently make sustainability or ESG claims may wish to review their marketing messaging prior to June to ensure that it is clear, fair and not misleading.
From July 2024 onwards, SDR will initially start with requirements for labelling, marketing, pre-contractual disclosures and customer facing disclosures. Following this will be a staggered rollout of additional reporting requirements, starting with the largest firms.
The investment classification and labelling rules would come into effect provisionally from 30 June 2024 for in-scope firms (other than portfolio managers) and 30 December 2024 for portfolio managers that satisfy the 90% test: where 90% or more of the value of the constituent products qualify for a label.
Notably, the use of labels is optional even for funds targeting retail investors, and may be used for funds targeting institutional investors.
A limited crossover between regulations
The overall level of convergence between SFDR and SDR may be lower than the market would have hoped. In terms of leveraging compliance efforts from SFDR and SDR, there is only limited crossover.
Learn how Sweep can help you comply with regulations and meet your climate targets