The double materiality concept refers to the recognition that sustainability reporting should consider both the impacts of organizations on society and the environment, as well as the influence of these external factors on the organizations themselves.
As sustainability and ESG considerations become increasingly important, understanding double materiality is crucial for businesses seeking to align their strategies with long-term sustainability goals. In this blog post, we will explore what materiality is, delve into the concept of double materiality, discuss its relevance in the context of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and other legislation, and provide insights into how businesses can prepare for this emerging reporting approach.
What is materiality?
Before delving into double materiality, it is important to understand the concept of materiality itself. How do we know what exactly a material impact is?
Materiality refers to the significance or relevance of information in decision-making processes. In sustainability reporting, materiality helps companies identify and prioritize the ESG issues that have the greatest impact on their performance and stakeholders’ interests. By focusing on material issues, companies ensure that their disclosures are informative and reflect their most important sustainability concerns.
What is double materiality?
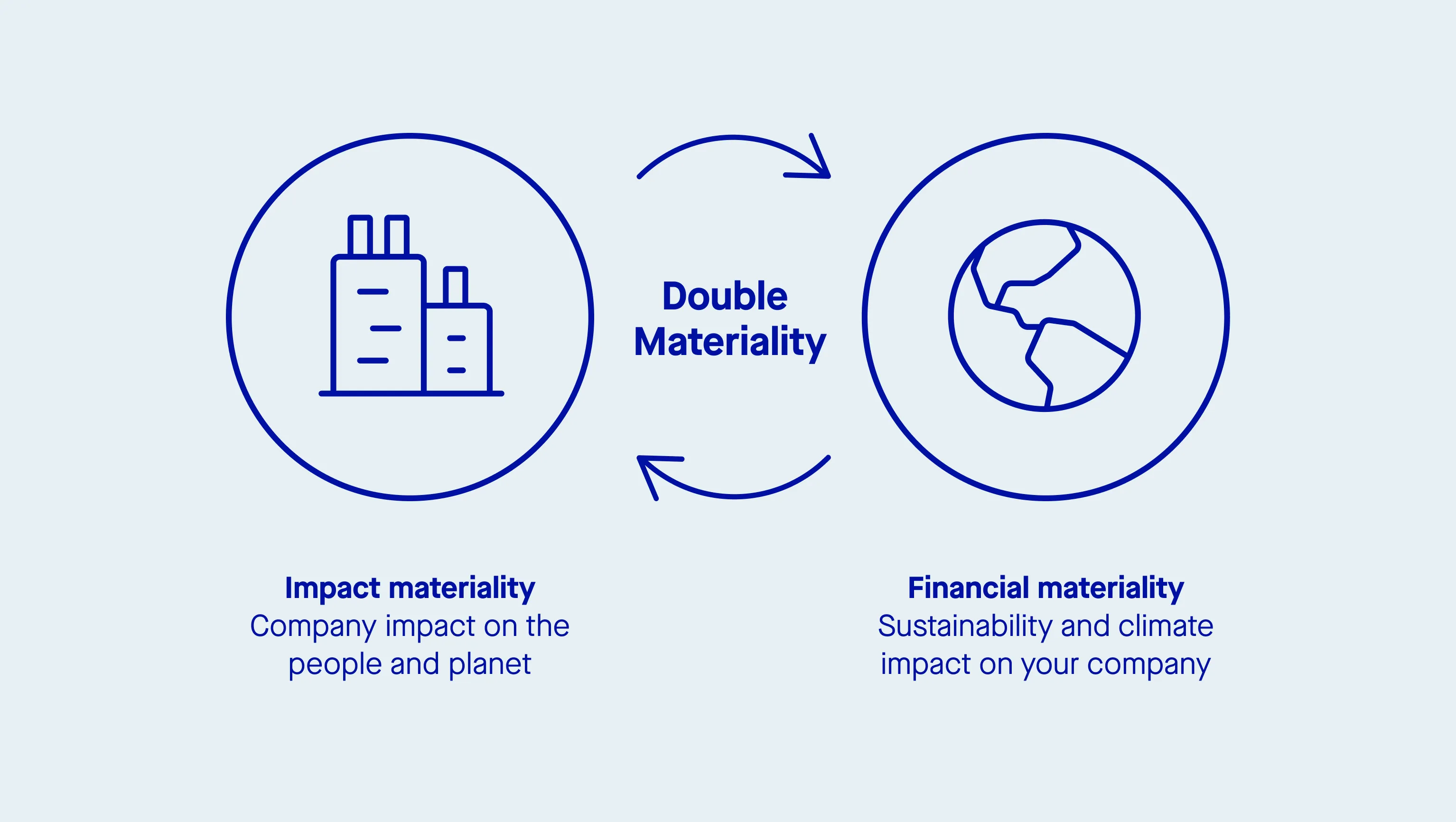
Double materiality extends the traditional concept of what accounting standards consider ‘material’ by recognizing that ESG issues not only affect a company’s financial performance (financial materiality) but also have broader societal and environmental impacts.
The concept outlines that a businesses and financial institutions should report simultaneously on sustainability matters that are financially material in influencing business value and at the same time material to the wider environment and society at large.
According to the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), when it comes to financial statements, information on a company is material and should be disclosed if “a reasonable person” would consider it important.
Double materiality recognizes that ESG factors can influence the long-term financial performance of a company and should, therefore, be integrated into decision-making processes and disclosed to stakeholders.
Background and framework
The concept of double materiality has its roots in the European Union’s (EU) regulatory framework for sustainability reporting. The EU’s Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) was a pioneering step, requiring large public interest entities to disclose information on environmental, social, and employee matters, respect for human rights, and issues related to bribery and corruption. This directive introduced a double materiality perspective, considering both the financial and non-financial impacts of a company’s activities. Building on the NFRD, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) aims to strengthen and expand these requirements.
Double materiality in sustainability reporting and the CSRD
The CSRD, proposed by the European Union, aims to enhance sustainability disclosure requirements for thousands of EU companies. One of the key features of the CSRD is the explicit recognition of double materiality. It highlights the need for companies to assess and disclose their impacts on society and the environment, as these factors can significantly influence their financial performance in the long run.
Other legislation featuring double materiality
The concept of double materiality is not exclusive to the CSRD. It is also prominent in other legislation and frameworks, which can directly affect corporate behaviour. For example, the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) recognizes the concept of double materiality in its reporting framework. Note that at the moment, the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) does not require companies to report using the double materiality concept.
Implications for businesses and preparation
For businesses, understanding what double materiality means, and accounting for it is essential for sustainable decision-making and effective reporting.
Assessing and managing ESG and financial risks
Assessing your ESG risks is crucial for understanding and mitigating potential impacts on your company’s operations, reputation, and capital allocation and financial stability. Start by evaluating your company’s impact on environmental, social, and governance factors to identify areas of vulnerability. Consider financial risks associated with climate change, such as physical risks, regulatory changes, and market shifts. These risks can have direct financial repercussions if not managed effectively. Additionally, assess human capital issues, including employee health and safety, diversity and inclusion, and talent management, as these can significantly impact your organization’s performance. By gathering and analyzing material information related to ESG risks, you can develop robust risk management strategies and enhance your resilience in an evolving business landscape.
Conducting a double materiality assessment
To conduct a double materiality assessment and start effectively managing climate-related risks, it is important to adopt a structured approach. Begin by engaging with internal and external stakeholders, seeking their input on the environmental impacts associated with climate change. It is crucial to adhere to disclosure regulations, including new rules and guidelines, especially those mandated by European regulators, to mitigate potential legal liabilities. Carefully analyze the feedback received from stakeholders and assess the potential significance of the identified issues. This will enable you to make informed decisions about your sustainability strategy and reporting. By proactively addressing emerging risks and prioritizing appropriate actions, you can demonstrate your organization’s commitment to sustainable practices while fulfilling reporting requirements.
Find out more about conducting materiality assessments here.
Implementation and best practices
Implementing double materiality requires a thorough materiality assessment to identify the sustainability issues most relevant to a company’s operations and stakeholders. This process involves evaluating both the financial and non-financial impacts of the company’s activities.
Best practices for implementing double materiality include:
- Engaging stakeholders: Involve investors, employees, customers, and other stakeholders to understand their expectations and concerns regarding sustainability issues.
- Conducting a Materiality Assessment: Identify and prioritize the most relevant sustainability issues that could impact the company’s performance and stakeholder interests.
- Developing a Comprehensive Reporting Framework: Create a sustainability reporting framework that includes both financial and non-financial information, ensuring a holistic view of the company’s impacts.
- Integrating Reporting: Ensure that sustainability reporting is seamlessly integrated into the company’s overall reporting framework, providing a consistent and transparent view of the company’s performance.
By following these best practices, companies can effectively implement double materiality, enhancing their sustainability reporting and aligning their strategies with long-term sustainability goals.
Challenges and future directions
Implementing double materiality can be challenging, especially for companies new to sustainability reporting. Some of the key challenges include:
- Defining materiality: Determining what constitutes a “material” sustainability issue can be complex and may vary across industries and stakeholders.
- Data collection and reporting: Gathering accurate and comprehensive data on sustainability performance requires robust systems and processes.
- Integration into reporting frameworks: Ensuring that sustainability reporting is integrated into the company’s overall reporting framework can be resource-intensive and requires a coordinated approach.
Despite these challenges, double materiality is a crucial step towards promoting transparency and accountability in sustainability reporting. The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) is working on developing a global guide for sustainability reporting that will incorporate double materiality. This initiative aims to provide a consistent framework for companies to report on their sustainability performance, facilitating comparability and reliability of information.
In the future, we can expect increased emphasis on double materiality in sustainability reporting. Companies will need to be more transparent and accountable, considering the broader impacts of their activities on the environment and society. This shift will not only enhance stakeholder trust but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient business landscape.
To summarize
Double materiality is a crucial concept in financial reporting and aligning investment activity with sustainability goals. It signifies a shift in focus from solely considering financial performance to recognizing the significance of broader societal and environmental impacts. In the context of the CSRD and similar regulations, it is imperative for businesses to conduct thorough assessments of their ESG impacts and disclose relevant information. By embracing double materiality, you can ensure that your strategies align with sustainability objectives, which not only enhances your company’s reputation but also builds stakeholder trust. Through this proactive approach, you contribute to a more sustainable future while reaping the benefits of long-term business resilience.