The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards are among the most widely used frameworks for sustainability reporting. Developed through a multi-stakeholder process, they provide a globally recognized structure for organizations to report on their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts in a consistent and transparent manner. GRI empowers organizations to measure and communicate their sustainability efforts, while aligning with international goals such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The Standards are designed to be flexible and applicable across all sectors and sizes of organizations, helping businesses identify and report on the sustainability topics most relevant to them. They provide a common language for organizations and stakeholders to understand and evaluate sustainability performance.
A flexible and modular reporting framework
The GRI Standards offer a modular system composed of three interrelated types of standards: universal, sector, and topic standards. Organizations use the universal standards as the foundation for all reporting. They then apply relevant topic standards to disclose on material topics and, where available, use sector standards to guide disclosures relevant to their specific industry. This modular structure enables organizations to create tailored sustainability reports while ensuring global comparability and transparency.
Importantly, the GRI Standards are regularly revised to reflect evolving sustainability challenges, stakeholder expectations, and best practices, ensuring that the framework remains rigorous yet practical.
Universal GRI Reporting standards (GRI 100 series)
The universal standards provide the foundation for sustainability reporting and apply to every organization using the GRI framework. These standards support organizations in identifying material topics and in communicating general information about their structure, governance, strategy, and stakeholder engagement.
The three core universal standards include:
- GRI 1: Foundation 2021 – Explains how to use the GRI Standards, outlines compliance requirements, and defines key reporting principles such as accuracy, balance, and verifiability.
- GRI 2: General Disclosures 2021 – Covers essential background about the reporting organization, including its size, activities, workers, supply chain, and governance.
- GRI 3: Material Topics 2021 – Guides organizations in identifying their material topics and outlines how to disclose them effectively, including the use of applicable topic and sector standards.
These standards establish the basis for meaningful and comparable disclosures and help organizations prepare comprehensive and high-quality sustainability reports.
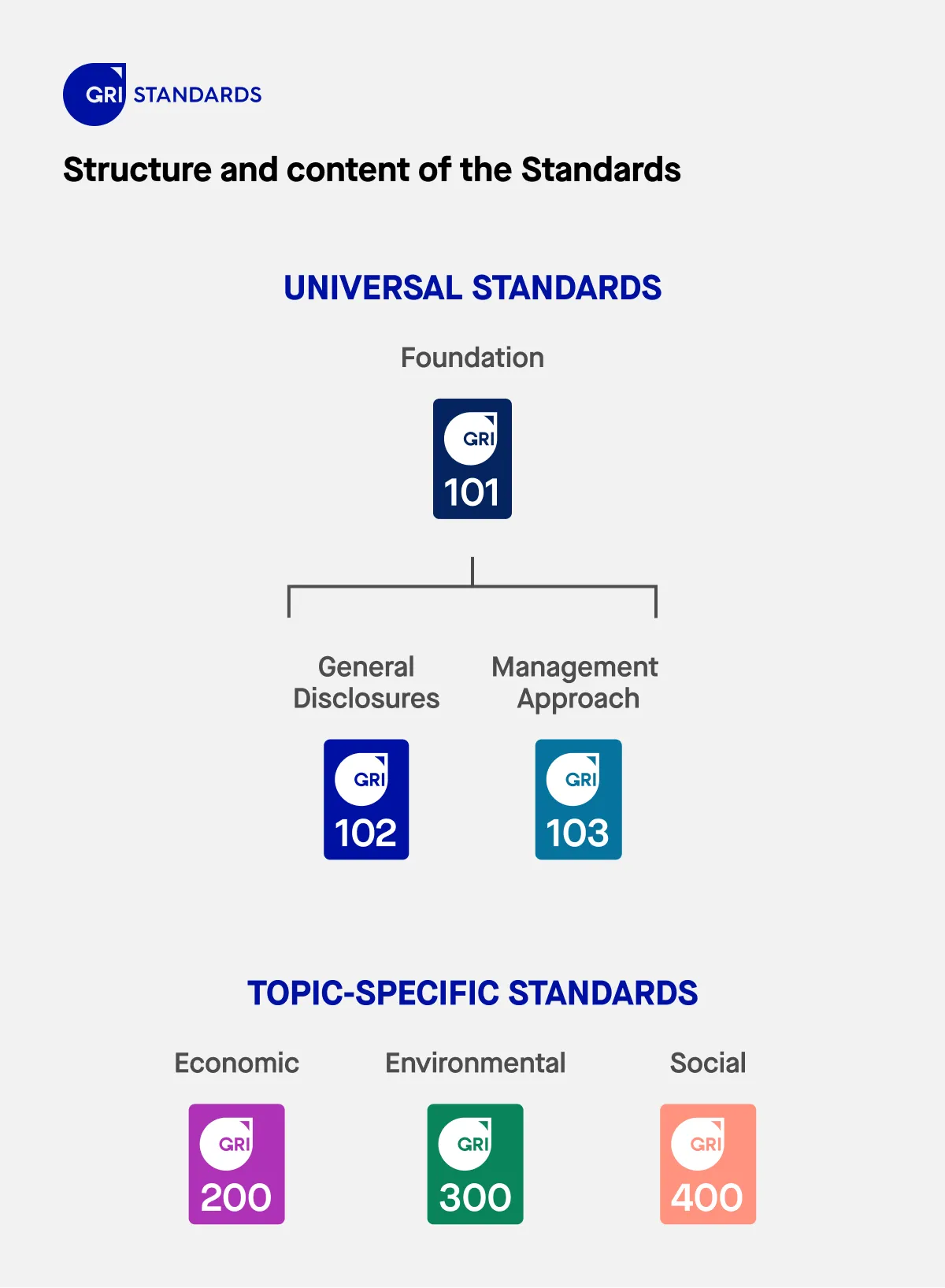
Topic standards (GRI 200, 300, 400 series)
The GRI Topic Standards are used by organizations to report in detail on their material sustainability topics. These standards are grouped into three series based on the three dimensions of sustainability: economic, environmental, and social.
GRI 200 series: Economic topics
The economic standards focus on an organization’s impact on the economic conditions of its stakeholders and the wider economy, rather than the financial performance of the organization itself. Topics in this series include anti-corruption, market presence, procurement practices, and indirect economic impacts.
For example, disclosures may include how an organization contributes to local economies, its approach to tax, or how it prevents corruption in its operations and value chains.
GRI 300 series: Environmental topics
The environmental standards examine an organization’s impact on natural systems, including land, air, water, and ecosystems. Topics in this series include energy, water and effluents, biodiversity, emissions, and waste.
For instance, GRI 306: Waste 2020 helps organizations disclose how they manage waste generation and disposal across their value chain. These disclosures promote better understanding of an organization’s environmental footprint and its efforts to mitigate impact.
GRI 400 series: Social topics
The social standards address an organization’s impacts on the social systems in which it operates. This includes issues like labor practices, human rights, diversity and inclusion, health and safety, and community relations.
These standards help organizations assess and communicate how they manage the well-being of workers, local communities, and other stakeholders, as well as how they handle grievance mechanisms and supply chain due diligence.
Each topic standard includes both management disclosures (how the topic is managed) and topic-specific disclosures (quantitative or qualitative data about the impacts).
GRI Sector standards
To enhance consistency and quality in reporting across industries, GRI has introduced sector standards. These are designed to reflect the most significant impacts and stakeholder expectations for a particular sector.
Sector standards provide tailored guidance by:
- Defining sector-specific sustainability impacts
- Highlighting likely material topics
- Linking to the most relevant topic standards
They help organizations focus their reporting on what matters most, reducing unnecessary disclosures and improving relevance. Each sector standard includes an overview of the sector’s characteristics, key risks and opportunities, and guidance on disclosures.
GRI has prioritized high-impact industries for the first round of sector standards. The first to be published was for the oil and gas sector, followed by coal, agriculture, aquaculture and fishing, and most recently, mining. Standards for financial services and textiles and apparel are currently under development.
Organizations are required to use relevant sector standards if available. This ensures better comparability within sectors and supports stakeholder decision-making through more complete and standardized disclosures.

A dynamic and evolving framework
One of the GRI Standards’ greatest strengths is their continuous evolution. The GRI frequently reviews and revises its standards to reflect new developments in sustainability and respond to the needs of organizations and stakeholders alike.
For example, the biodiversity topic standard was updated in January 2024 and will become effective in 2026. These updates are informed by expert input, scientific research, international frameworks, and public consultations.
This responsiveness helps organizations stay aligned with current expectations and practices, ensuring that sustainability disclosures remain relevant and impactful.
How to use the GRI Standards
To use the GRI Standards effectively, organizations should begin by defining the scope and boundaries of their sustainability reporting—determining which activities, products, and services are covered. A key step in this process is conducting a materiality assessment to identify the most relevant sustainability topics, such as climate change, that impact both the organization and its stakeholders.
Once these topics are clear, companies can select the appropriate GRI Standards aligned with their reporting criteria. These global standards for sustainability offer a structured approach for disclosing management strategies, performance data, and key indicators.
By applying the Standards consistently, organizations can communicate their impacts transparently and drive continuous improvement in sustainability performance.
Why adopt the GRI Standards?
Using the GRI Standards provides a range of benefits to organizations and their stakeholders:
- Transparency and accountability – By reporting in accordance with GRI, organizations demonstrate openness and integrity in how they manage their ESG impacts.
- Materiality focus – The GRI approach ensures that reports are centered around the most important topics, improving the relevance and decision-usefulness of information.
- Stakeholder engagement – GRI supports stakeholder-inclusive reporting, helping organizations respond to the concerns of investors, regulators, employees, communities, and customers.
- Global alignment – GRI’s collaboration with initiatives like the UN Global Compact and SDGs supports international sustainability commitments and reporting harmonization.
- Comparability and credibility – The structured format allows stakeholders to compare sustainability performance across companies and sectors with confidence.
How ESG software supports GRI reporting
ESG software helps streamline and strengthen GRI-aligned reporting by providing:
- Pre-mapped GRI frameworks to guide disclosure alignment
- Centralized data collection across ESG topics
- Real-time insights to foresee and act on sustainability risks
- Automated workflows for consistent, transparent reporting
- Training tools and guidance to build internal reporting capacity
- Verifiable, audit-ready records to meet stakeholder expectations
By using ESG software, organizations can simplify compliance and enhance the quality of their sustainability disclosures.
Getting started with the GRI reporting process
The GRI Standards offer a rigorous yet practical framework for organizations seeking to measure and communicate their sustainability impacts. By providing universal, topic-specific, and sector-based guidance, GRI enables organizations to produce tailored, high-quality reports that reflect their material issues and contribute to responsible business practices.
Whether your organization is just starting its sustainability journey or enhancing existing disclosures, the GRI Standards provide the tools needed to meet stakeholder expectations, align with global goals, and drive long-term value.
For the most recent updates, tools, and guidance, visit the official GRI website.