The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is one of the most widely used sustainability reporting frameworks for sustainability reporting, empowering organizations worldwide to measure and disclose their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts. It provides a rigorous and standardized approach to reporting, ensuring transparency and helping businesses create sustainable practices.
In this article, we’ll explore the key features of the GRI, how it works, and its impact on driving positive change in sustainability practices across industries.
GRI overview: A global multi-stakeholder process
Founded in 1997, the GRI emerged from the merger of the Coalition for Environmental Responsible Economies (CERES) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Since its inception, it has worked to develop and refine rigorous yet practical standards for sustainability reporting, establishing itself as a global leader for sustainability . As an independent international organization, the GRI has set the standard for transparent reporting on economic impacts, environmental issues, and social factors, empowering organizations to adopt a transparent reporting approach.
The GRI sustainability reporting standards are widely recognized as global best practices for measuring and communicating an organization’s ESG impacts, offering building blocks for responsible business practices.
How does the GRI work?
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) collaborates closely with the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC) to support organizations in aligning their reporting with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Together, they work to unlock positive change by providing resources like the SDG Compass, and promoting best reporting practices among businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This collaboration ensures that organizations report their policies and activities in a way that contributes to global sustainability goals.
The role of the Global Sustainability Standards Board (GSSB)
The Global Sustainability Standards Board (GSSB) is responsible for developing and maintaining the GRI Standards. This independent body ensures that the GRI remains relevant, rigorous, and aligned with international best practices. The GSSB’s work helps ensure that organizations have the tools they need to assess their sustainability performance accurately and consistently.
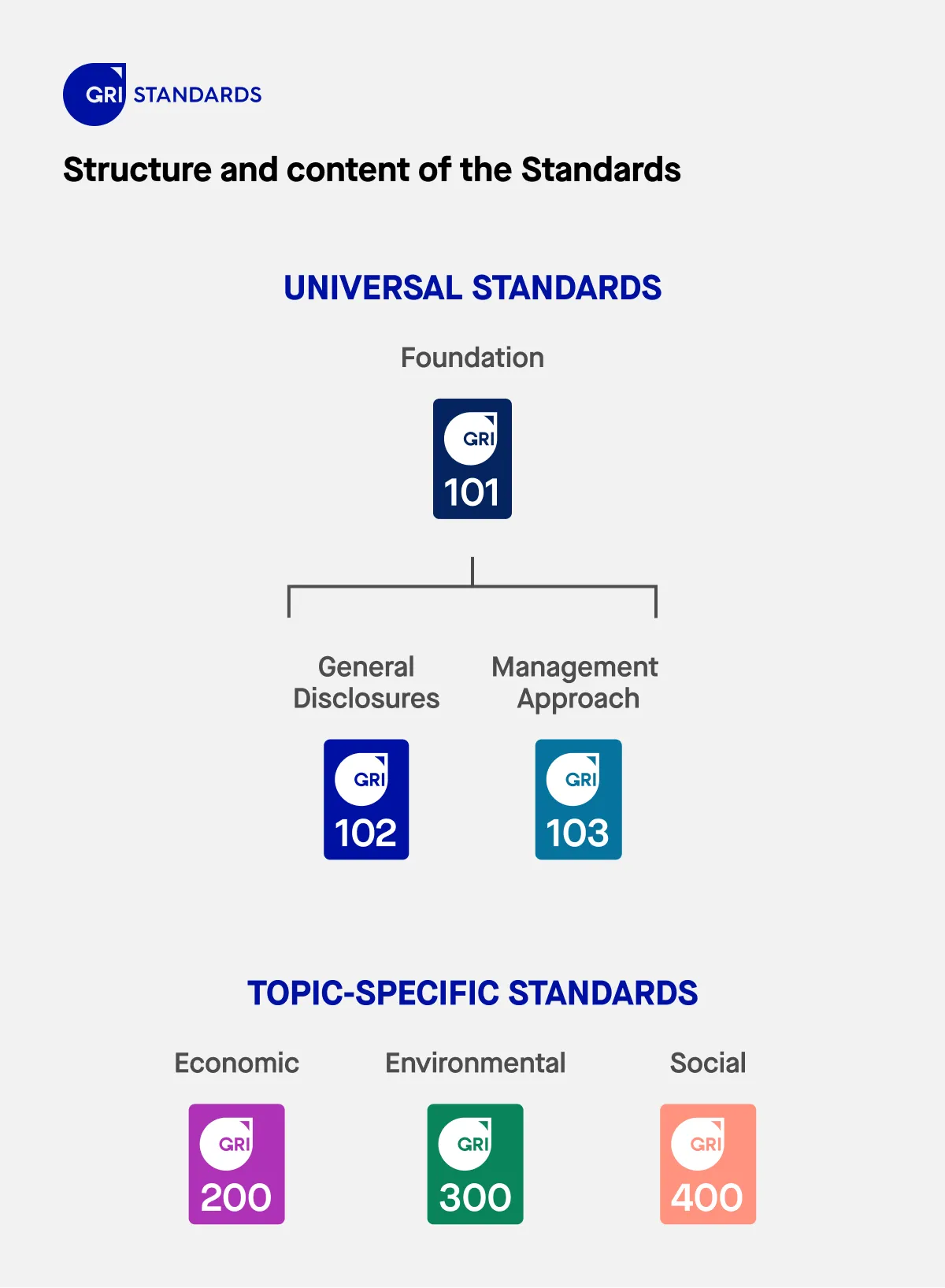
What are the GRI Standards?
The GRI Standards provide a comprehensive framework to help organizations measure, manage, and report their sustainability performance. These standards cover a wide range of economic, environmental, and social topics, offering organizations the flexibility to prioritize the issues most relevant to their stakeholders.
The standards are designed to ensure that businesses can effectively report their ESG impacts in a transparent and comparable manner, helping stakeholders assess the organization’s sustainability performance over time.
Who should use the GRI Standards?
The standards are applicable to organizations of all types, sizes, and sectors. Whether you’re a large multinational corporation or a small-medium enterprise (SME), the standards provide a flexible framework to measure and disclose your sustainability impacts. These standards are also suitable for non-profit organizations, government agencies, and public sector entities, ensuring that sustainability information is accessible to a wide range of stakeholders, including investors, regulators, and communities.
Benefits of applying the GRI Standards
By adhering to the standards, your organization can enjoy several key benefits:
Enhanced credibility and transparency – Implementing the standards enhances the credibility of your sustainability reports, demonstrating a commitment to transparent reporting and helping build trust with stakeholders. This is critical in fostering positive relationships with investors, customers, and employees.
Focus on materiality – The standards emphasize materiality, helping organizations focus on the most relevant sustainability issues to their industry and stakeholders. This ensures that reports reflect real and potential impacts, offering greater value to decision-makers.
Alignment with global sustainability goals – The standards help your organization align with global sustainability frameworks like the SDGs, positioning your business as a responsible leader in sustainability and contributing to global goals.
Competitive advantage – By adopting the standards, your organization can create sustainable value and differentiate itself in the marketplace, demonstrating commitment to responsible business practices and building a competitive edge.
Categories of GRI Standards
The standards are organized into different modules:
Universal Standards
The universal GRI standards apply to all organizations, covering general information about the organization and its management of material sustainability topics. Every organization using the GRI framework must comply with the Universal Standards.
Sector Standards
The GRI sector standards focus on the most material issues for specific industries, helping organizations narrow down the most relevant topics for their sector. The GRI has developed sector-specific standards for 40 industries with significant sustainability impacts.
Topic Standards
The Topic Standards outline required and recommended disclosures for various sustainability topics, guiding organizations in reporting on specific material issues relevant to their operations. These standards ensure that disclosures are consistent and aligned with global best practices.
GRI reporting principles
To ensure high-quality sustainability reporting, organizations must follow the GRI reporting principles:
- Accuracy – Provide precise, verifiable data that reflects the organization’s true impact.
- Balance – Report both positive and negative impacts for an unbiased view.
- Clarity – Ensure that information is easy to understand for readers.
- Comparability – Report data consistently, enabling meaningful comparisons over time.
- Completeness – Include sufficient information to assess your organization’s impact comprehensively.
- Sustainability Context – Place your organization’s impacts within the broader sustainable development context.
- Timeliness – Provide information on a regular schedule.
- Verifiability – Ensure that the information disclosed can be verified by third parties.
Steps to report in accordance with the GRI Standards
1. Determine data availability
Evaluate your organization’s internal capabilities to meet the GRI Standards requirements.
2. Apply the reporting principles
Align your reporting approach with the GRI principles, ensuring that your report reflects the most relevant and accurate information.
3. Assess materiality
Identify and prioritize material sustainability topics for your organization, considering both internal and external impacts.
4. Collect and disclose information
Gather data and present it according to the GRI Standards to ensure completeness and accuracy in your reporting.
5. Compile the GRI content index
Create a content index that links your disclosures to the corresponding sections in your report, making it easy for stakeholders to navigate your report.
6. Publish your disclosures
Distribute your GRI-aligned report publicly, ensuring transparency and accessibility to stakeholders.
7. Register your report
Notify the GRI about your use of the GRI Standards, ensuring that your report is verified and recognized.
GRI and CSRD: complementary approaches
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) work together to improve sustainability transparency. While the GRI provides a flexible, globally recognized framework for ESG reporting, the CSRD requires more detailed disclosures for companies in Europe. By adopting both, organizations can align with regulatory requirements and voluntary standards, ensuring transparent reporting and stronger sustainability practices.
A common global language for sustainability reporting
The GRI is a global leader for sustainability reporting. By adopting these standards, businesses can create sustainable long term value, enhance their credibility, align with global sustainability goals, better manage risks and opportunities, and support strategic decision making.
How ESG software supports GRI reporting
ESG software helps organizations streamline sustainability reporting by providing the tools and services support needed for transparent disclosure. Key benefits include:
- Automated data collection – Reduces manual effort and ensures accuracy in tracking environmental, social, and economic impacts.
- Real-time insights – Enables companies to foresee and act on sustainability risks and opportunities.
- Compliance support – Aligns reporting with rigorous yet practical sustainability standards, ensuring adherence to GRI requirements.
- Training tools and services – Provides guidance on reporting best practices and recent developments in sustainability reporting.
- Enhanced transparency – Helps organizations meet the expectations of diverse stakeholders with verifiable, high-quality ESG data.
By integrating ESG software, companies can simplify sustainability reporting and strengthen their long-term ESG strategy.