IFRS S1 is a critical standard introduced by the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation to guide businesses in disclosing sustainability-related financial information. The global focus on sustainability is rising, and businesses must align with this shift by providing transparent and comparable sustainability-related financial disclosures. In this guide, we will explore the main objectives of IFRS S1, its scope, and how businesses can apply this standard to their annual reporting periods.
The objective of IFRS S1 is clear: to ensure that companies disclose relevant sustainability-related risks and opportunities that could materially impact their long-term financial performance. This not only helps investors but also aligns the company’s operations with the broader expectations of stakeholders, society, and regulatory bodies. The goal is to enable better decision-making and resource allocation based on sustainability considerations.
What is the main objective of the IFRS S1?
The primary objective of IFRS S1 is to require businesses to disclose sustainability-related risks and opportunities that could reasonably be expected to affect their cash flows and long-term viability. In particular, the standard focuses on risks that arise from environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors—commonly referred to as sustainability-related risks. These risks can significantly affect how a business operates, its access to finance, and its cost of capital.
Sustainability-related financial information includes disclosures about how businesses interact with their stakeholders, society, the economy, and the environment. These disclosures help investors understand the long-term viability of a business by highlighting how these interactions might impact financial performance and business prospects.
Incorporating sustainability-related risks into decision-making is essential because the financial success of a company in the long term is often determined by its ability to adapt to and manage these risks. For example, businesses that fail to disclose climate-related risks may overlook critical vulnerabilities, which could harm their financial health over time.
What is the scope of IFRS S1?
IFRS S1 applies to all businesses that prepare general purpose financial reports, regardless of the accounting framework used, including those following International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), or other local reporting standards. This broad scope ensures that the standard can be applied consistently across different jurisdictions and industries.
According to IFRS S1, businesses must disclose sustainability-related financial information relevant to their overall strategy, risk management, governance processes, and performance related to climate-related risks and other sustainability-related matters. These disclosures must cover all areas where sustainability-related risks or opportunities could potentially affect a business’s financial performance, access to capital, or long-term viability.
IFRS S1 emphasizes that sustainability-related risks and opportunities should be evaluated across the entire value chain of the business, including all interactions, resources, and relationships that are integral to creating and delivering a company’s products and services. The standard further clarifies that sustainability-related disclosures should cover a range of topics such as governance, strategy, risk management, and key sustainability metrics.
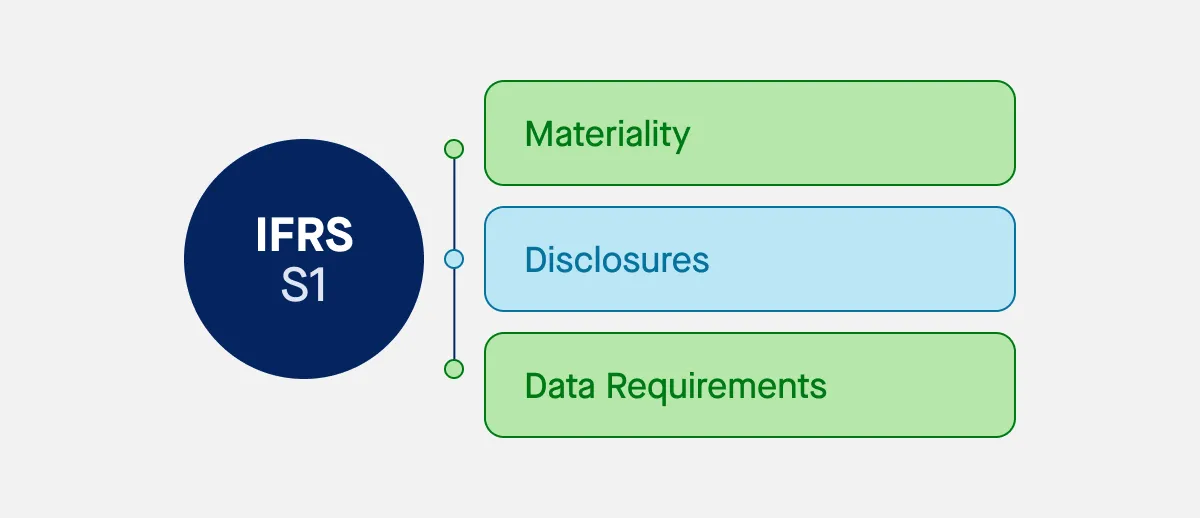
What is ‘materiality’ and how does it feature in IFRS S1?
Materiality is a central concept in IFRS S1. In the context of sustainability-related financial disclosures, information is deemed material if omitting, misstating, or obscuring it could reasonably influence the decisions of users of general purpose financial reports. Essentially, if a piece of information could impact investors’ decisions regarding the provision of resources to a business, it is considered material.
For example, if a company operates in an industry heavily affected by climate-related risks, such as a mining company or an oil and gas firm, it must disclose relevant climate-related risks, as they are material to the company’s financial performance. However, information that does not significantly influence the company’s financial outlook or investment attractiveness would be considered immaterial and may not need to be disclosed.
IFRS S1 guides businesses in determining what is material, requiring companies to consider all facts and circumstances and decide how to aggregate or disaggregate information in their disclosures. This ensures that businesses provide users of general purpose financial reports with a clear, concise, and meaningful depiction of sustainability-related risks and opportunities.
How can businesses disclose information for the IFRS S1?
When preparing their sustainability-related financial disclosures, businesses must adhere to a clear structure set out by IFRS S1. This structure helps ensure that disclosures are both comprehensive and comparable, providing stakeholders with useful insights into how sustainability-related risks affect the business.
There are several key requirements for disclosure:
Governance
Companies must disclose the governance processes and controls in place to monitor and manage sustainability-related risks and opportunities. This includes board oversight, management accountability, and the integration of sustainability into the company’s broader governance framework.
Strategy
Companies should outline their strategy for managing sustainability-related risks and opportunities. This includes how they intend to mitigate risks, seize opportunities, and integrate sustainability into their long-term strategic objectives.
Risk Management
Disclosures should provide insight into how a company identifies, assesses, prioritizes, and manages sustainability-related risks. This section of the disclosure should describe both the processes in place and how they are integrated into the broader risk management framework of the organization.
Metrics and Targets
To provide transparency, companies should disclose key metrics and targets for managing sustainability-related risks. These disclosures should include the company’s performance on sustainability indicators and its progress toward any goals it has set, including emissions reductions or the achievement of diversity and inclusion objectives.
The ultimate goal of these disclosures is to ensure that the information provided is useful for making informed decisions about the company’s long-term value and sustainability. These disclosures should be aligned with the broader financial reports, ensuring a cohesive and comprehensive overview of the company’s performance.
The ISSB and IFRS S2
The ISSB (International Sustainability Standards Board), which oversees the development of IFRS S1, plays a crucial role in promoting global consistency in sustainability-related financial disclosures. The ISSB’s overarching goal is to create a comprehensive global baseline for sustainability reporting that investors can use to make better decisions.
Moreover, IFRS S1 works alongside other standards, such as IFRS S2, which focuses specifically on climate-related disclosures. While IFRS S1 outlines the general requirements for sustainability-related financial information, IFRS S2 dives deeper into the specifics of climate-related risks and opportunities. This includes guidelines for reporting on emissions, climate-related financial risks, and the financial impact of climate-related factors on a business’s operations.
Together, these standards help businesses identify, assess, and manage sustainability-related risks, especially those arising from climate change. For businesses to comply fully with the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards, they must ensure that their disclosures on sustainability risks and opportunities, including climate-related risks, align with both IFRS S1 and IFRS S2.
The Importance of Sustainability-Related Financial Information
As the world becomes more focused on ESG (environmental, social, and governance) factors, sustainability-related financial information is gaining prominence. The disclosure of sustainability-related financial information allows businesses to showcase how their operations are aligned with broader environmental and social goals while also highlighting how sustainability-related risks could affect their financial performance.
For example, companies in industries such as manufacturing or agriculture must assess their exposure to climate-related risks, like changes in weather patterns or resource scarcity. By disclosing sustainability-related financial information, companies can not only demonstrate their commitment to mitigating risks but also attract investors who are increasingly interested in supporting businesses with strong sustainability practices.
Disclosures about climate-related risks, in particular, are essential in helping investors understand how a company’s financial health may be influenced by the transition to a low-carbon economy. Businesses need to make these disclosures to ensure that they remain competitive and attractive to investors who are prioritizing sustainable investments.
Moving Forward with IFRS S1
For businesses, complying with IFRS S1 and the broader IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards represents a significant step toward greater transparency and accountability regarding sustainability-related risks and opportunities. By adopting these standards, businesses can demonstrate that they are proactively managing sustainability-related risks, which can ultimately lead to improved financial performance and increased investor confidence.
The role of the ISSB in driving global alignment on sustainability disclosures cannot be understated. As the ISSB works alongside other international organizations, including the GRI (Global Reporting Initiative) and the SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board), it will continue to evolve the landscape of sustainability reporting, ensuring that businesses are equipped with the right tools to navigate sustainability challenges.
In conclusion, IFRS S1 is a critical step toward integrating sustainability considerations into financial reporting. By complying with these standards, businesses not only meet the expectations of investors but also position themselves for long-term success in a rapidly changing world. The shift toward sustainability reporting is here to stay, and businesses that embrace these changes will be well-positioned to thrive in the years to come.
How can sustainability software support ISSB data collection?
As ISSB standards require detailed and structured sustainability-related financial disclosures, companies need efficient tools to manage data collection and reporting. Sustainability software can support ISSB compliance by:
- Automating data gathering from various business operations
- Ensuring alignment with IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards
- Providing real-time tracking of sustainability performance
- Facilitating accurate reporting of ISSB-mandated sustainability metrics
- Enhancing risk assessment and scenario analysis for climate-related disclosures
By leveraging sustainability software, companies can streamline their reporting processes and ensure compliance with ISSB requirements while improving the quality and reliability of sustainability-related financial information.